An Identity Access Management (IAM) system is a framework that manages and controls who can access resources, ensuring secure and authorised access.
Key Features of an IAM system:
- User authentication: Verifies user identity.
- Access control: Manages permissions.
- Single sign-on (SSO): One login for all.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Adds extra security layers.
- Role-based access: Assigns roles to users.
- Audit logs: Tracks user activities.
- Etc.
Challenge: Complex User Management
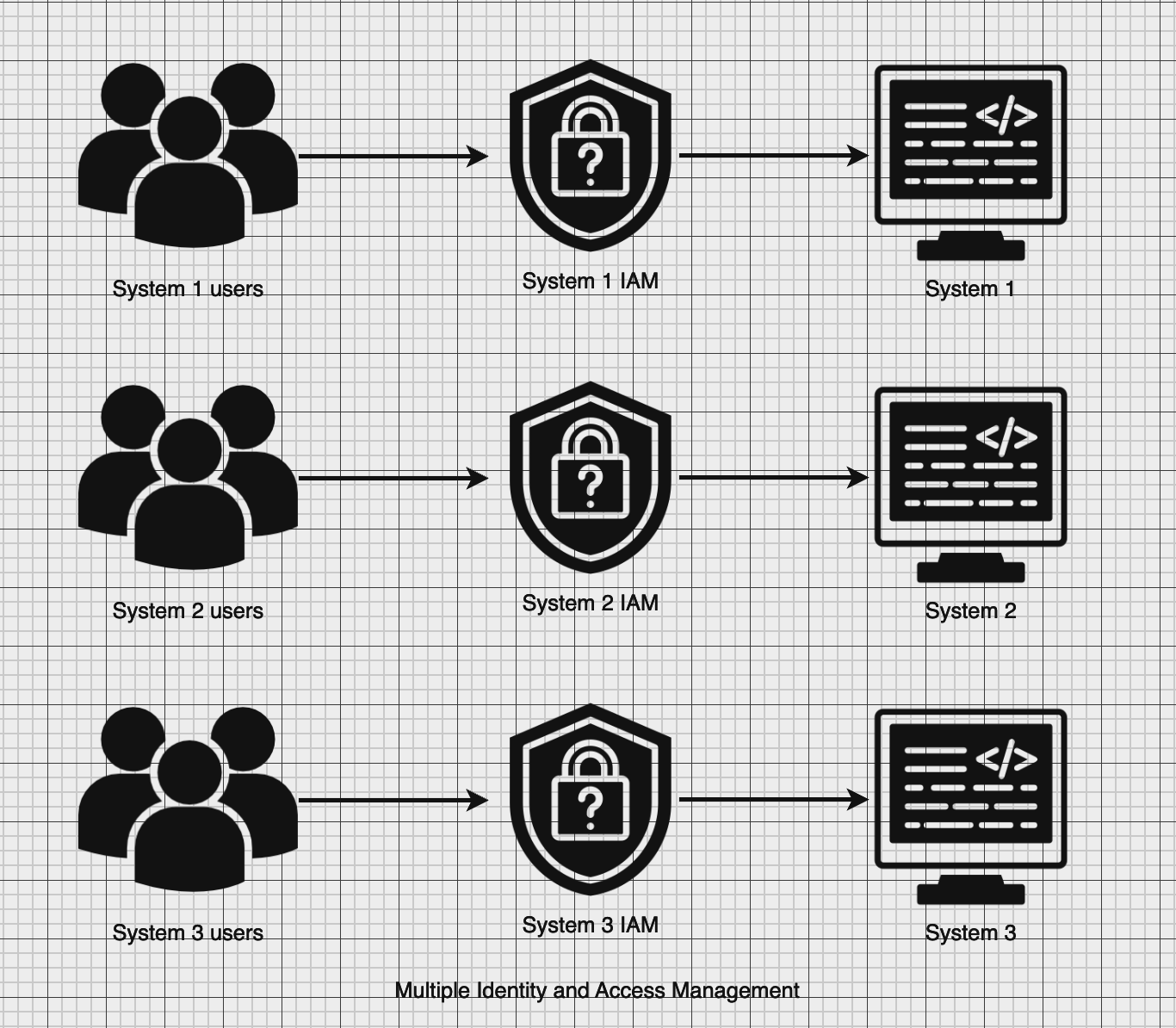
As the number of government systems increases, there is an increased complexity in user management with the following consequences:
- Custom user management for each system Increased development effort: Each system having to manage its own users and authentication increases development effort, requiring more resources. User management is also really hard to get right, with increased security vulnerabilities.
Solution: Unified Identity and Access Management
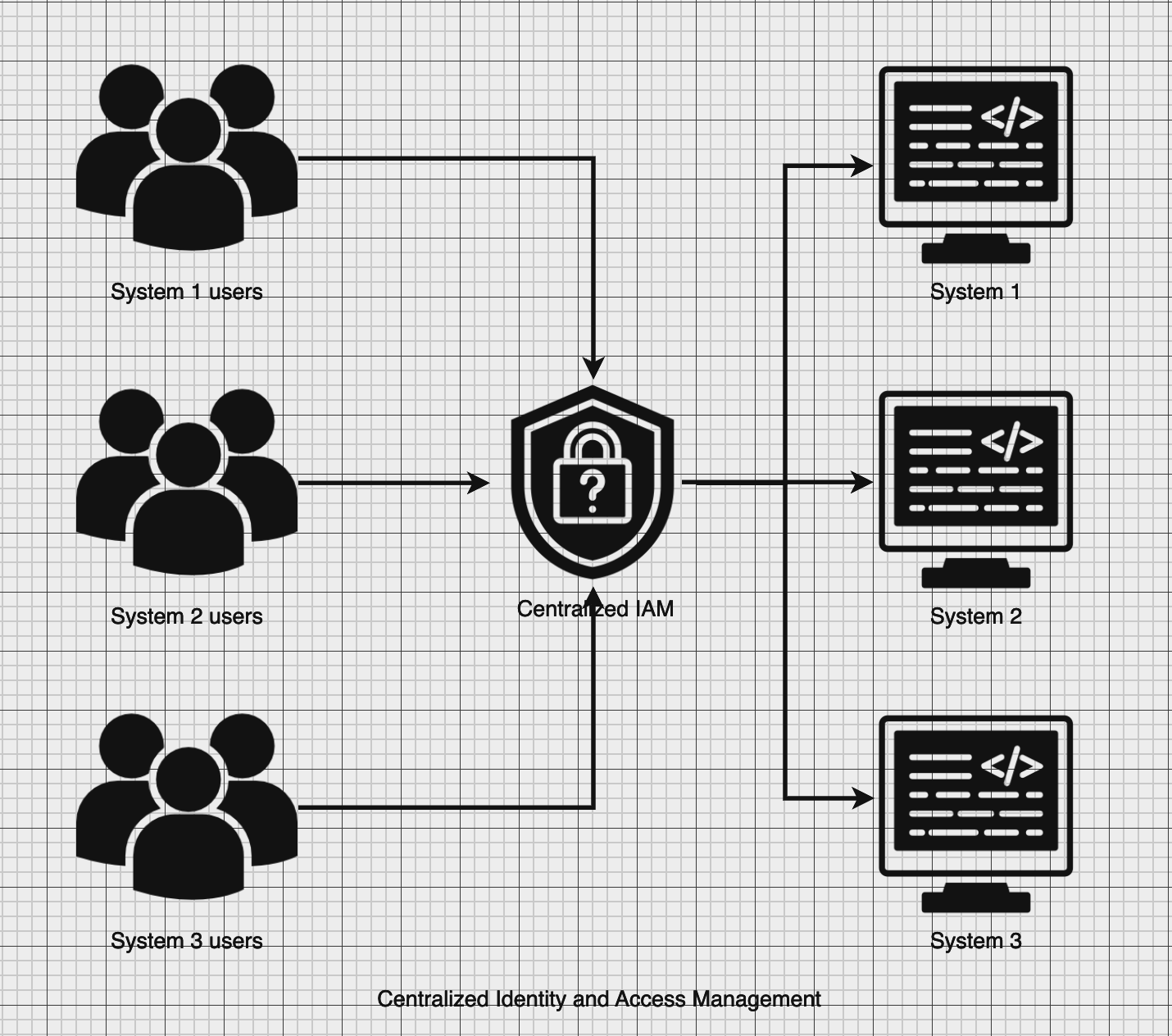
Centralizing identity and access management can have the following benefits:
- Delegated Identity & Access Management. Delegating identity and access management to an external system can increase the security and scalability of systems. This also reduces development efforts, optimising resource utilisation.
- Single Sign-On: With a single account and session, users can authenticate in multiple systems, improving user experience.